Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Reference Ranges of Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3: Results from a Multicenter Study in Healthy Korean Adults
- In-Kyung Jeong, Jong Kyu Byun, Junghyun Noh, Sang Wan Kim, Yoon-Sok Chung, Tae Sun Park, Sung-Woon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):954-959. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.785
- 4,444 View
- 125 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
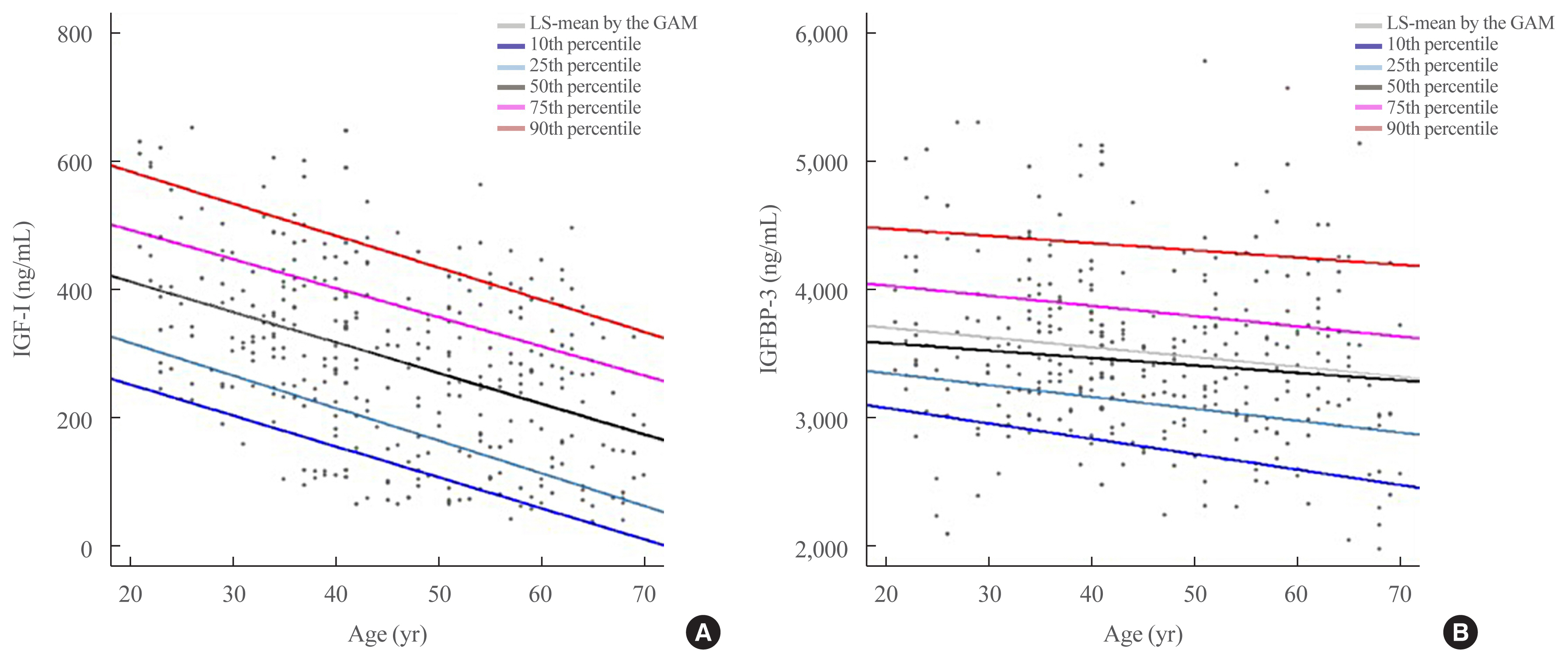
ePub - Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis and treatment of growth hormone (GH) excess or deficiency. The GH study group of the Korean Endocrine Society aims to establish the Korean reference ranges of serum IGF-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and assess the relationship between IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and clinical parameters. Fasting serum was collected from healthy Korean adults at health promotion centers of five hospitals nationwide. Serum IGF-I and IGFBP-3 were measured via an immunoradiometric assay using a DSL kit (Diagnostic Systems Laboratories). Serum samples from 354 subjects (180 male, 174 female) were analyzed based on sex at 10-year intervals from 21 to 70 years. IGF-I levels were inversely correlated with age. After adjustment of age, the IGF-I/IGFBP-3 ratio was significantly negatively associated with blood pressure and free thyroxine and positively associated with weight, hemoglobin, creatinine, alanine transferase, fasting glucose, and thyroid stimulating hormone. Therefore, age- and sex-specific reference ranges of serum IGF-I and IGFBP-3 can be efficient in evaluating GH excess or deficiency in Korean population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Capillary blood as a complementary matrix for doping control purposes. Application to the definition of the individual longitudinal profile of IGF-1
Carlotta Stacchini, Francesco Botrè, Xavier de la Torre, Monica Mazzarino
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis.2023; 227: 115274. CrossRef
- Capillary blood as a complementary matrix for doping control purposes. Application to the definition of the individual longitudinal profile of IGF-1

- Miscellaneous
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Position Statement from Korean Endocrine Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology
- Jung Hee Kim, Hyun Wook Chae, Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyeong Hye Park, Dong Jun Lim, Kwang Joon Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Gyuri Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Seong Hee Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Yul Hwangbo, Ju Hee Lee, Bu Kyung Kim, Yong Jun Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Hwa Young Ahn, Hoon Sung Choi, Sang Mo Hong, Dong Yeob Shin, Ji A Seo, Se Hwa Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hoon Yu, Byung Joon Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sung-Woon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):272-287. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.272
- 9,519 View
- 429 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
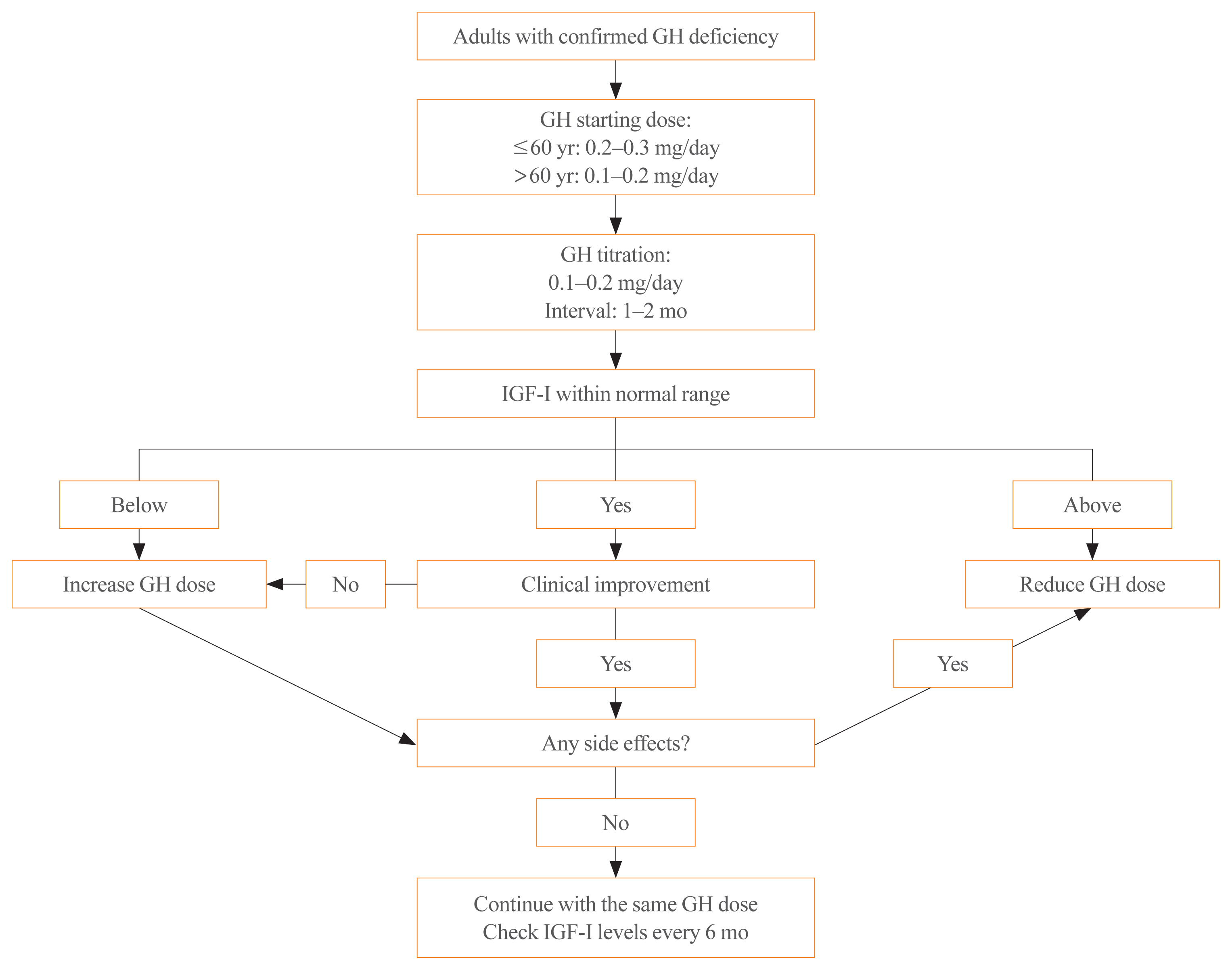
ePub - Growth hormone (GH) deficiency is caused by congenital or acquired causes and occurs in childhood or adulthood. GH replacement therapy brings benefits to body composition, exercise capacity, skeletal health, cardiovascular outcomes, and quality of life. Before initiating GH replacement, GH deficiency should be confirmed through proper stimulation tests, and in cases with proven genetic causes or structural lesions, repeated GH stimulation testing is not necessary. The dosing regimen of GH replacement therapy should be individualized, with the goal of minimizing side effects and maximizing clinical improvements. The Korean Endocrine Society and the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology have developed a position statement on the diagnosis and treatment of GH deficiency. This position statement is based on a systematic review of evidence and expert opinions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial
Ghina Tsurayya, Cut Alifiya Nazhifah, Muhammad Rahmat Pirwanja, Putri Oktaviani Zulfa, Muhammad Raihan Ramadhan Tatroman, Fajar Fakri, Muhammad Iqhrammullah
Children.2024; 11(2): 227. CrossRef - Efficacy, safety, and patient satisfaction of norditropin and sogroya in patients with growth hormone deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Obieda Altobaishat, Mohamed Abouzid, Mostafa Hossam El Din Moawad, Abdulrahman Sharaf, Yazan Al-Ajlouni, Tungki Pratama Umar, Abdallah Bani-salameh, Mohammad Tanashat, Omar Abdullah Bataineh, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Adult Height in Patients with Non-Permanent Idiopathic GH Deficiency
Agnese Murianni, Anna Lussu, Chiara Guzzetti, Anastasia Ibba, Letizia Casula, Mariacarolina Salerno, Marco Cappa, Sandro Loche
Endocrines.2023; 4(1): 169. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests
Soo Yeun Sim, Moon Bae Ahn
Sensors.2023; 23(15): 6892. CrossRef - The risk patients with AGHD have of developing CVD
Eisha Javed, Maha Zehra, Naz Elahi
International Journal of Cardiology Cardiovascular Risk and Prevention.2023; 19: 200221. CrossRef - Diagnosis of GH Deficiency Without GH Stimulation Tests
Anastasia Ibba, Sandro Loche
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Impacts of Discontinuation and Resumption of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment during the Transition Period in Patients with Childhood-Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency
Yun Jeong Lee, Yunha Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Han Saem Choi, Ho-Seong Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Jung Eun Moon, Cheol Woo Ko, Moon Bae Ahn, Byung-Kyu Suh, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 359. CrossRef - A Radiomics-Based Model with the Potential to Differentiate Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature on Sella MRI
Taeyoun Lee, Kyungchul Song, Beomseok Sohn, Jihwan Eom, Sung Soo Ahn, Ho-Seong Kim, Seung-Koo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(9): 856. CrossRef - Phenotypic spectrum of patients with mutations in CHD7: clinical implications of endocrinological findings
Ja Hye Kim, Yunha Choi, Soojin Hwang, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Endocrine Disorders: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Hyemi Kwon, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Kyung Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 839. CrossRef - Laron syndrome: clinic, diagnostics (а clinical case)
P.M. Lіashuk, R.P. Lіashuk, N.I. Stankova, M.B. Kudina
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(3): 193. CrossRef - Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 322. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Guidelines for Adrenal Tumor Ablation
Byung Kwan Park, Masashi Fujimori, Shu-Huei Shen, Uei Pua
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 553. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation guidelines for renal cell carcinoma
Byung Kwan Park, Shu-Huei Shen, Masashi Fujimori, Yi Wang
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2021; 62(4): 378. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency
Jung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2021; 96(5): 400. CrossRef
- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
- Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong Jun Lim, Dong Yeob Shin, Se Hwa Kim, Min Jeong Kwon, Ha Young Kim, Jin Hwa Kim, Dong Sun Kim, Chong Hwa Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):53-62. Published online March 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.53
- 6,482 View
- 254 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub The Korean Endocrine Society (KES) published clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acromegaly in 2011. Since then, the number of acromegaly cases, publications on studies addressing medical treatment of acromegaly, and demands for improvements in insurance coverage have been dramatically increasing. In 2017, the KES Committee of Health Insurance decided to publish a position statement regarding the use of somatostatin analogues in acromegaly. Accordingly, consensus opinions for the position statement were collected after intensive review of the relevant literature and discussions among experts affiliated with the KES, and the Korean Neuroendocrine Study Group. This position statement includes the characteristics, indications, dose, interval (including extended dose interval in case of lanreotide autogel), switching and preoperative use of somatostatin analogues in medical treatment of acromegaly. The recommended approach is based on the expert opinions in case of insufficient clinical evidence, and where discrepancies among the expert opinions were found, the experts voted to determine the recommended approach.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hydrogel-fiber-mesh-based 3D cell cultures: A new method for studying pituitary tumors
Wooju Jeong, Sungrok Wang, Yumin Kim, Soohyun Lee, Minhu Huang, Jaeil Park, Myung-Han Yoon, Chang-Myung Oh, Cheol Ryong Ku
Smart Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: A Position Statement of the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Ho-Cheol Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 175. CrossRef - Growth Hormone Excess: Implications and Management
Suneela Dhaneshwar, Shrishti Shandily, Vatsalya Tiwari
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2023; 23(6): 748. CrossRef - Revisiting the usefulness of the short acute octreotide test to predict treatment outcomes in acromegaly
Montserrat Marques-Pamies, Joan Gil, Elena Valassi, Marta Hernández, Betina Biagetti, Olga Giménez-Palop, Silvia Martínez, Cristina Carrato, Laura Pons, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Marta Araujo-Castro, Concepción Blanco, Inmaculada Simón, Andreu Simó-Servat, Gemm
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: a Position Statement from the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Hwa Young Ahn, Bu Kyung Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, So Young Park, Min-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Sun Wook Cho, Ho-Cheol Kang
International Journal of Thyroidology.2022; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Octreotide in the treatment of acromegaly – the possibilities of high-dose therapy
I. A. Ilovayskaya
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (10): 148. CrossRef - Approach of Acromegaly during Pregnancy
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mara Carsote, Ana Valea, Andreea Gabriela Nicola, Ionela Teodora Dascălu, Tiberiu Tircă, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Mihaela Jana Țuculină
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2669. CrossRef - Left to themselves: Time to target chronic pain in childhood rare diseases
Christine B. Sieberg, Alyssa Lebel, Erin Silliman, Scott Holmes, David Borsook, Igor Elman
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2021; 126: 276. CrossRef - Severe respiratory failure in a patient with COVID-19 and acromegaly: rapid improvement after adding octreotide
Jacob Luty, LesleAnn Hayward, Melanie Jackson, P Barton Duell
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(8): e243900. CrossRef - Precision Therapy in Acromegaly Caused by Pituitary Tumors: How Close Is It to Reality?
Cheol Ryong Ku, Vladimir Melnikov, Zhaoyun Zhang, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 206. CrossRef - Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2019; 94(6): 485. CrossRef
- Hydrogel-fiber-mesh-based 3D cell cultures: A new method for studying pituitary tumors

- Adrenal gland
- Clinical Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cushing's Disease in Korea
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Jung Hee Kim, Byung Joon Kim, Min-Seon Kim, Eun Jig Lee, Sung-Woon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):7-18. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.7
- 6,749 View
- 152 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Cushing's disease (CD) is a rare disorder characterized by the overproduction of adrenocorticotropic hormone due to a pituitary adenoma that ultimately stimulates excessive cortisol secretion from the adrenal glands. Prior to the detection of pituitary adenomas, various clinical signs of CD such as central obesity, moon face, hirsutism, and facial plethora are usually already present. Uncontrolled hypercortisolism is associated with metabolic, cardiovascular, and psychological disorders that result in increased mortality. Hence, the early detection and treatment of CD are not only important but mandatory. Because its clinical manifestations vary from patient to patient and are common in other obesity-related conditions, the precise diagnosis of CD can be problematic. Thus, the present set of guidelines was compiled by Korean experts in this field to assist clinicians with the screening, diagnoses, and treatment of patients with CD using currently available tests and treatment modalities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diet quality and dietary acid load in relation to cardiovascular disease mortality: Results from Fasa PERSIAN cohort study
Sahar Fereidouni, Najmeh Hejazi, Reza Homayounfar, Mojtaba Farjam
Food Science & Nutrition.2023; 11(3): 1563. CrossRef - Role of computed tomography in predicting adrenal adenomas with cortisol hypersecretion
Chan Kyo Kim, Kyung A Kang, Young Lyun Oh, Sung Yoon Park
The British Journal of Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary acid load and mortality from all causes, CVD and cancer: results from the Golestan Cohort Study
Ehsan Hejazi, Hadi Emamat, Maryam Sharafkhah, Atoosa Saidpour, Hossein Poustchi, Sadaf Sepanlou, Masoud Sotoudeh, Sanford Dawsey, Paolo Boffetta, Christian C Abnet, Farin Kamangar, Arash Etemadi, Akram Pourshams, Akbar Fazeltabar Malekshah, Paul Berennan,
British Journal of Nutrition.2022; 128(2): 237. CrossRef - Forty Years Together, New Leap Forward! The 40th Anniversary of the Korean Endocrine Society
Jong Chul Won, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 851. CrossRef - Pituitary adenomas: current principles of diagnosis and treatment
L. I. Astafyeva, I. V. Chernov, I. V. Chekhonin, E. I. Shults, I. N. Pronin, P. L. Kalinin
Russian journal of neurosurgery.2021; 22(4): 94. CrossRef - Metabolic changes in serum steroids for diagnosing and subtyping Cushing’s syndrome
Chang Ho Ahn, Chaelin Lee, Jaeyoon Shim, Sung Hye Kong, Su-jin Kim, Yong Hwy Kim, Kyu Eun Lee, Chan Soo Shin, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2021; 210: 105856. CrossRef - Application of different variants of endoscopic transphenoidal removal of corticotropinomas in order to increase the frequency and duration of remission
A. Ashraf, I. V. Chernov, A. N. Shkarubo, M. A. Kutin, D. V. Fomichev, O. I. Sharipov, Yu. Yu. Trunin, D. N. Andreev, A. A. Abdilatipov, L. I. Astafieva, B. Abdali, A. B. Kurnosov, G. E. Chmutin, Kalinin P. L. Kalinin P. L.
Vestnik nevrologii, psihiatrii i nejrohirurgii (Bulletin of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery).2021; (2): 143. CrossRef - Modern aspects of surgery for cushing’s disease
A. Abdali, L.I. Astafeva, Yu.Yu. Trunin, I.V. Chernov, Yu.G. Sidneva, A.A. Abdilatipov, P.L. Kalinin
Voprosy neirokhirurgii imeni N.N. Burdenko.2021; 85(4): 111. CrossRef - Pituitary microadenomas — current diagnostic and treatment methods
L.I. Astafyeva, B.A. Kadashev, Yu.G. Sidneva, I.V. Chernov, P.L. Kalinin
Voprosy neirokhirurgii imeni N.N. Burdenko.2020; 84(2): 110. CrossRef - Usefulness of prolactin measurement in inferior petrosal sinus sampling with desmopressin for Cushing’s syndrome
Hamideh Akbari, Mohammad Ghorbani, Maryam Kabootari, Ali Zare Mehrjardi, Mohammad Reza Mohajeri Tehrani, Mojtaba Malek, Mohammad E. Khamseh
British Journal of Neurosurgery.2020; 34(3): 253. CrossRef - Hormonal aggressiveness according to the expression of cellular markers in corticotroph adenomas
Jung Soo Lim, Mi-Kyung Lee, Eunhee Choi, Namki Hong, Soo Il Jee, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrine.2019; 64(1): 147. CrossRef - Clinical Parameters to Distinguish Silent Corticotroph Adenomas from Other Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas
Daham Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Se Hee Park, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Sun Ho Kim, Eun Jig Lee
World Neurosurgery.2018; 115: e464. CrossRef - Blood Tests for the Diagnosis of Adrenal Diseases
Seon-Ah Cha, Sung-Dae Moon
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2018; 93(6): 532. CrossRef - Choosing wisely: la lista del gruppo di studio Endocrinologia e Malattie del Metabolismo della Società Italiana di Patologia Clinica e Medicina di Laboratorio
Romolo M. Dorizzi, Anna Ferrari, Marina Vitillo, Beatrice Caruso, Claudio Cocco, Erennio Ciotoli, Federica D’Aurizio, Elisa Esposito, Germana Giannone, Giulio Ozzola, Ottavia Porzio, Emanuela Toffalori, Renato Tozzoli
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio - Italian Journal of Laboratory Medicine.2016; 12(2): 81. CrossRef - Surgical management of adrenocorticotropic hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas
Edwin S Kulubya, Daniel A Donoho, John D Carmichael, Gabriel Zada
International Journal of Endocrine Oncology.2016; 3(1): 41. CrossRef
- Diet quality and dietary acid load in relation to cardiovascular disease mortality: Results from Fasa PERSIAN cohort study

- Thyroid
- Celiac Disease in a Predisposed Subject (HLA-DQ2.5) with Coexisting Graves' Disease
- In Kyoung Hwang, Seon Hye Kim, Unjoo Lee, Sang Ouk Chin, Sang Youl Rhee, Seungjoon Oh, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sung-Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim, Suk Chon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):105-109. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.105
- 3,748 View
- 32 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Celiac disease is an intestinal autoimmune disorder, triggered by ingestion of a gluten-containing diet in genetically susceptible individuals. The genetic predisposition is related to human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II genes, especially HLA-DQ2-positive patients. The prevalence of celiac disease has been estimated to be ~1% in Europe and the USA, but it is rarer and/or underdiagnosed in Asia. We report a case of celiac disease in a predisposed patient, with a HLA-DQ2 heterodimer, and Graves' disease that was treated successfully with a gluten-free diet. A 47-year-old woman complained of persistent chronic diarrhea and weight loss over a 9 month period. Results of all serological tests and stool exams were negative. However, the patient was found to carry the HLA DQ2 heterodimer. Symptoms improved after a gluten-free diet was initiated. The patient has been followed and has suffered no recurrence of symptoms while on the gluten-free diet. An overall diagnosis of celiac disease was made in a genetically predisposed patient (HLA-DQ2 heterodimer) with Graves' disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Celiac Disease Genetics, Pathogenesis, and Standard Therapy for Japanese Patients
Tasuku Tamai, Kenji Ihara
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2075. CrossRef - Underutilization of diagnostic assays for celiac disease in Korea
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Olmesartan is not associated with the risk of enteropathy: a Korean nationwide observational
cohort study
Seng Chan You, Hojun Park, Dukyong Yoon, Sooyoung Park, Boyoung Joung, Rae Woong Park
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(1): 90. CrossRef - Prevalence of celiac disease in Asia: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Prashant Singh, Shubhangi Arora, Alka Singh, Tor A Strand, Govind K Makharia
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2016; 31(6): 1095. CrossRef
- Celiac Disease Genetics, Pathogenesis, and Standard Therapy for Japanese Patients

- Adrenal gland
- Acromegaly due to a Macroinvasive Plurihormonal Pituitary Adenoma and a Rectal Carcinoid Tumor
- Sang Ouk Chin, Jin-Kyung Hwang, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Seungjoon Oh, Misu Lee, Natalia S. Pellegata, Sung-Woon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):389-394. Published online January 5, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.389
- 3,726 View
- 41 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader A macroinvasive pituitary adenoma with plurihormonality usually causes acromegaly and hyperprolactinemia, and also accompanies with neurologic symptoms such as visual disturbances. However, its concurrent presentation with a rectal carcinoid tumor is rarely observed. This study reports the history, biochemical, colonoscopic and immunohistochemical results of a 48-year-old female with acromegaly and hyperprolactinemia. Despite the large size and invasive nature of the pituitary adenoma to adjacent anatomical structures, she did not complain of any neurologic symptoms such as visual disturbance or headache. Immunohistochemical staining of the surgical specimen from the pituitary adenoma revealed that the tumor cells were positive for growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Staining for pituitary-specific transcription factor-1 (Pit-1) was shown to be strongly positive, which could have been possibly contributing to the plurihormonality of this adenoma. Colonoscopy found a rectal polyp that was identified to be a carcinoid tumor using immunohistochemical staining. A macroinvasive pituitary adenoma with concomitant rectal carcinoid tumor was secreting GH, PRL, and TSH, which were believed to be in association with over-expression of Pit-1. This is the first case report of double primary tumors comprising a plurihormonal pituitary macroadenoma and rectal carcinoid tumor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Characteristics and Management of Cosecreting Thyroid Stimulating Hormone or Prolactin Pituitary Growth Hormone Adenomas: A Case-Control Study
Caiyan Mo, Han Chen, Jian Xu, Ying Guo, Yao Wang, Zheng Li, Tao Tong, Songbai Gui, Liyong Zhong
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Growth Hormone Excess: Implications and Management
Suneela Dhaneshwar, Shrishti Shandily, Vatsalya Tiwari
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2023; 23(6): 748. CrossRef - Pleiomorphism plurihormonal Pit-1-positive macroadenoma with central hyperthyroidism: a rare case report and literature review
Guiliang Peng, Chuanhong Guo, Yangfan Lv, Dandan Li, Ling Zhou, Rufei Shen, Yong Chen, Xin Zheng, Zheng Sun, Hongting Zheng, Min Long
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Characteristics and Management of Cosecreting Thyroid Stimulating Hormone or Prolactin Pituitary Growth Hormone Adenomas: A Case-Control Study

- Bone Metabolism
- Efficacy of a Once-Monthly Pill Containing Ibandronate and Cholecalciferol on the Levels of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Bone Markers in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis
- In-Jin Cho, Ho-Yeon Chung, Sung-Woon Kim, Jae-Won Lee, Tae-Won Lee, Hye-Soon Kim, Sin-Gon Kim, Han Seok Choi, Sung-Hee Choi, Chan Soo Shin, Ki-Won Oh, Yong-Ki Min, Jung-Min Koh, Yumie Rhee, Dong-Won Byun, Yoon-Sok Chung, Jeong Hyun Park, Dong Jin Chung, Minho Shong, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Ki Hyun Baek, Moo-Il Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):272-279. Published online December 9, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.272
- 4,520 View
- 47 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The present study evaluated the efficacy of a combination of ibandronate and cholecalciferol on the restoration of the levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) and various bone markers in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.
Methods This was a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, prospective 16-week clinical trial conducted in 20 different hospitals. A total of 201 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis were assigned randomly to one of two groups: the IBN group, which received a once-monthly pill containing 150 mg ibandronate (
n =99), or the IBN+ group, which received a once-monthly pill containing 150 mg ibandronate and 24,000 IU cholecalciferol (n =102). Serum levels of 25(OH)D, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and various bone markers were assessed at baseline and at the end of a 16-week treatment period.Results After 16 weeks of treatment, the mean serum levels of 25(OH)D significantly increased from 21.0 to 25.3 ng/mL in the IBN+ group but significantly decreased from 20.6 to 17.4 ng/mL in the IBN group. Additionally, both groups exhibited significant increases in mean serum levels of PTH but significant decreases in serum levels of bone-specific alkaline phosphatase and C-telopeptide of type 1 collagen (CTX) at 16 weeks; no significant differences were observed between the groups. However, in subjects with a vitamin D deficiency, IBN+ treatment resulted in a significant decrease in serum CTX levels compared with IBN treatment.
Conclusion The present findings demonstrate that a once-monthly pill containing ibandronate and cholecalciferol may be useful for the amelioration of vitamin D deficiency in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Moreover, this treatment combination effectively decreased serum levels of resorption markers, especially in subjects with a vitamin D deficiency, over the 16-week treatment period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of vitamin D supplementation or fortification on bone turnover markers in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Nasrin Nasimi, Sanaz Jamshidi, Aida Askari, Nazanin Zolfaghari, Erfan Sadeghi, Mehran Nouri, Nick Bellissimo, Shiva Faghih
British Journal of Nutrition.2024; 131(9): 1473. CrossRef - Quality of life and patient satisfaction with raloxifene/cholecalciferol combination therapy in postmenopausal women
Dong-Yun Lee, Yoon-Sok Chung
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of risedronate with cholecalciferol on bone mineral density in Korean patients with osteoporosis
So Young Park, Moo-Il Kang, Hyung Moo Park, Yumie Rhee, Seong Hwan Moon, Hyun Koo Yoon, Jung-Min Koh, Jae Suk Chang, In Joo Kim, Ye Yeon Won, Ye Soo Park, Hoon Choi, Chan Soo Shin, Taek Rim Yoon, Sung-Cheol Yun, Ho-Yeon Chung
Archives of Osteoporosis.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of vitamin D3 B.O.N intramuscular injection in Korean adults with vitamin D deficiency
Han Seok Choi, Yoon-Sok Chung, Yong Jun Choi, Da Hea Seo, Sung-Kil Lim
Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia.2016; 2(4): 228. CrossRef - Pharmacologic treatment of osteoporosis
Yong-Ki Min
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2016; 59(11): 847. CrossRef
- Effect of vitamin D supplementation or fortification on bone turnover markers in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



